What is Melanin

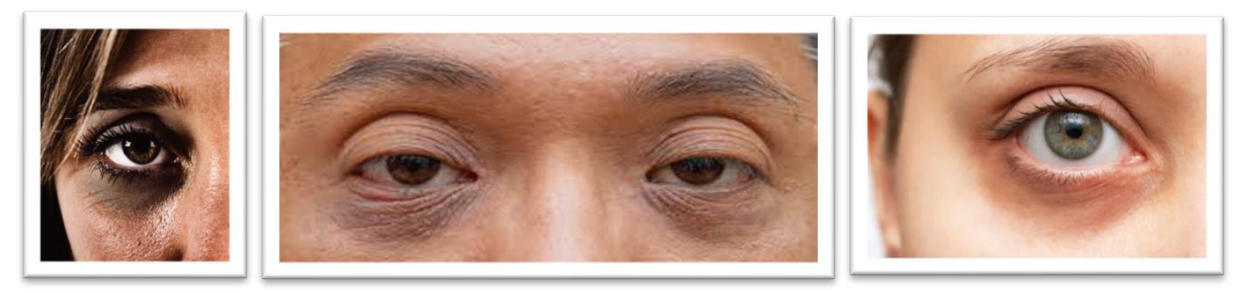
Melanin cause the dark spot at the skin
Skin covers the whole-body, protects it from any harmful environmental substances and becomes the first line of defense from any possible treat to the immunity system. There are a wide range of skin colors representing various races and ethnicities from all over the world. Skin tone colors vary from pale(light), fair, and medium to brown, dark brown and black.
Besides skin, the color of hair and eyes are also unique and different, rooting to many factors including different type of people from several continents, inherited genetics and sub- locations. As discussed in the previous chapter, skin has 3 main layers, namely epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The determination of skin, hair and eye color happens solely in the epidermis layer where the melanin is produced.

Melanin is a term used to describe a large group of related molecules responsible for many biological functions, mainly pigmentation of skin and hair and photoprotection of skin and eye (1). In the epidermis layer, deep down close to the basal layer, melanocytes are found. Melanocytes contain spherical shaped melanosomes which are also referred as factories for melanin. Inside the melanosomes, some important chemical reactions take place and turn the amino acid, Tyrosine into melanin. The proportion of two main forms of melanin produced, a reddish-yellow type verses a black-brown type, the total amount of melanin in each melanosome and the number of melanosomes in the epidermis, all vary from person to person and determine their skin colour.
Even though melanosomes are the melanin factories, in order for melanin to function, melanosomes need to be transported to the keratinocytes via melanocytes long projections. Then, inside keratinocytes, some melanosomes form a cap around the cell nucleus. This is where the most vital and notable function of melanin can be seen. The melanin inside the melanosome absorbs the ultraviolet energy from sunlight, reducing the amount of ultraviolet radiation that reaches the nucleus and the DNA inside the nucleus. These reactions clearly portray how melanin protects the skin from the harmful UV rays including UVA, UVB, UVC and blue light. UV radiation can cause DNA mutations that can lead to cancer. When UV radiation increases, melanin production increases and more melanosomes are delivered to keratinocytes.
The table below shows the three main forms of melanin exist in humans (2):

Additionally, melanin level inside the skin is affected by some factors; age, UV light exposure, inflammation and changes in hormone levels. When too much of melanin is produced, hyperpigmentation occurs. Other conditions that are strongly related to the increase production of melanin are Addison’s disease, hemochromatosis and pregnancy. All in all, melanin is undoubtedly crucial for skin welfare, functionality and overall skin health.
In accordance to the need of skin, melanin could be a life savior and great protector against multiple acute chronic diseases especially skin cancer. Nevertheless, too much or too less production of melanin can trigger other unwanted illnesses as well. Therefore, one should acquire more knowledge about the beauty and the beast of melanin to secure a better skin performance and suitable required pigmentation.
(1) Maranduca MA, Branisteanu D, Serban DN, Branisteanu DC, Stoleriu G, Manolache N, Serban IL. Synthesis and physiological implications of melanic pigments. Oncol Lett. 2019 May;17(5):4183-4187. (2) Daniel I. Schlessinger; McDamian Anoruo; Joel Schlessinger.biochemistry of melanin. NationalLibarary of medicine.1 May 2023.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459156/